
I had a few hours to spare the other day and I created the diagram (sketch) above trying to understand Colin Moock’s take in the subject. One post won’t cover all the ins and outs of this Design Pattern but its more of a review and study of the author’s view.
If we follow closely the diagram (sketch) this are the steps that should be taken:
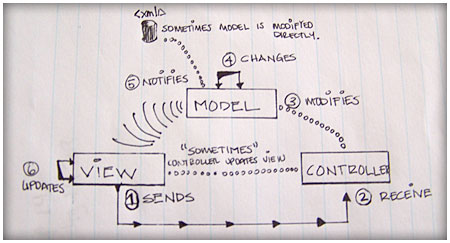
1 View sends user input to the Controller.
2 Controller receives the information that the View has sent to the Controller.
3 The Controller modifies the Model.
4 Now the Model changes itself using the information received.
5 The Model notifies the View of the changes
6 The View updates itself to reflect the changes requested.
Couple of things to note:
With this set up the Model might receive information directly and notify the View of those changes, for example a Database request or a XML load to the model. This might be a little different to other setups where the Controller always receives the information, even if it comes from an outside source.
Another thing to note is that sometimes the information that the View has sent to the Controller might be enough to update itself so the step to modify the Model is skipped completely.
Now, accordingly to the book point of view the Model and View can never live without each other, meaning that if you create a View it must have a Model for that specific view but if you decide to switch a View you must switch its Model as well and vice-versa. Now that is a little bit different to what the GOF describe in their book but that is a whole different post.
Short Notes:
Model: Data & Logic
View: Interface
Controller: Process Information
Long Notes:
Model:
- Stores properties
- Implements application methods
- provides methods to register current View(s)
- notify View(s) of changes
- implements application logic
View:
- creates interface
- Updates interface when Model changes
Controller:
- Cosmetic changes
- Updates View
- Translates user input to change the Model
you dont know what you are talking about.
MVC – Ñто не паттерн, а архитектура … ÐºÐ¾Ñ‚Ð¾Ñ€Ð°Ñ Ð² Ñвою очередь, например, включает в ÑÐµÐ±Ñ Ñ‚Ð°ÐºÐ¸Ðµ три фундаментальных паттерна: Model – View – Controller